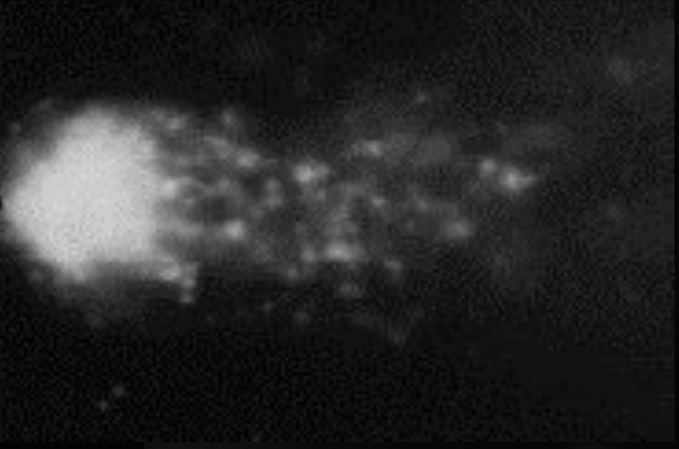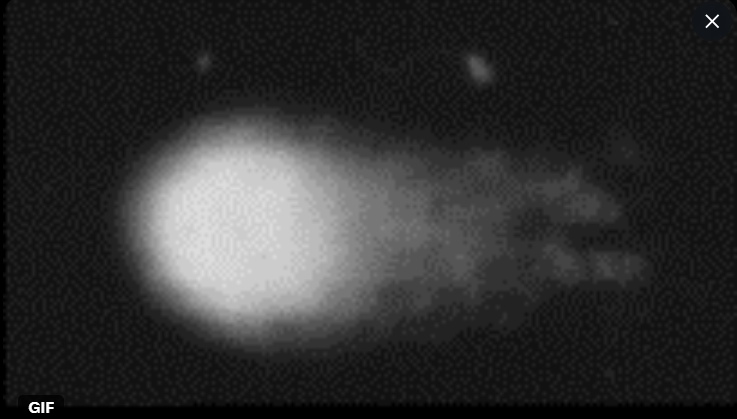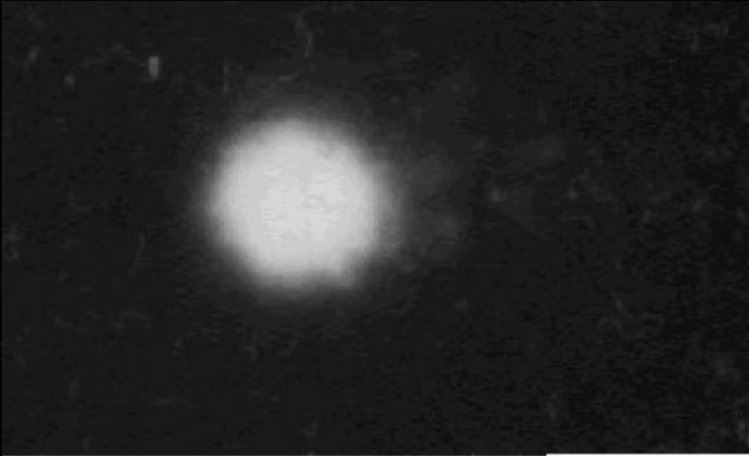
Control Cell (Unexposed DNA)
This is the baseline: DNA is a compact, intact bundle with almost no “comet tail.” Under normal lab conditions, spontaneous strand breaks are rare and quickly repaired.
Key Points:
• Serves as the “zero damage” reference.
• Minimal DNA fragmentation under standard conditions.
• Any tail in other conditions is above this spontaneous background.